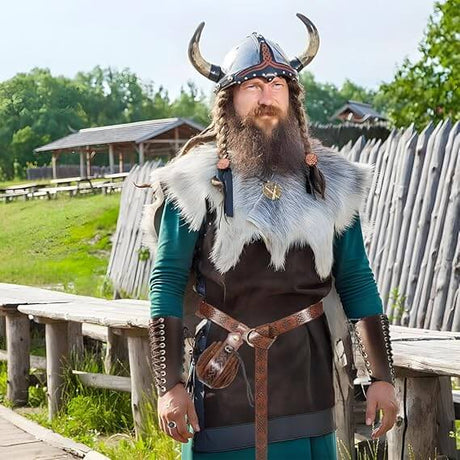
The Vikings, with their longships, daring raids, and rich mythology, have captured the imagination of people for centuries. But where did these seafaring warriors originate, and what drove them to embark on their legendary expeditions across Europe and beyond? In this blog, we'll explore the true origins of the Vikings, unraveling the mystery of their homeland, culture, and the distinction between Norse, Nordic, and Scandinavian identities.
The Origins of the Vikings

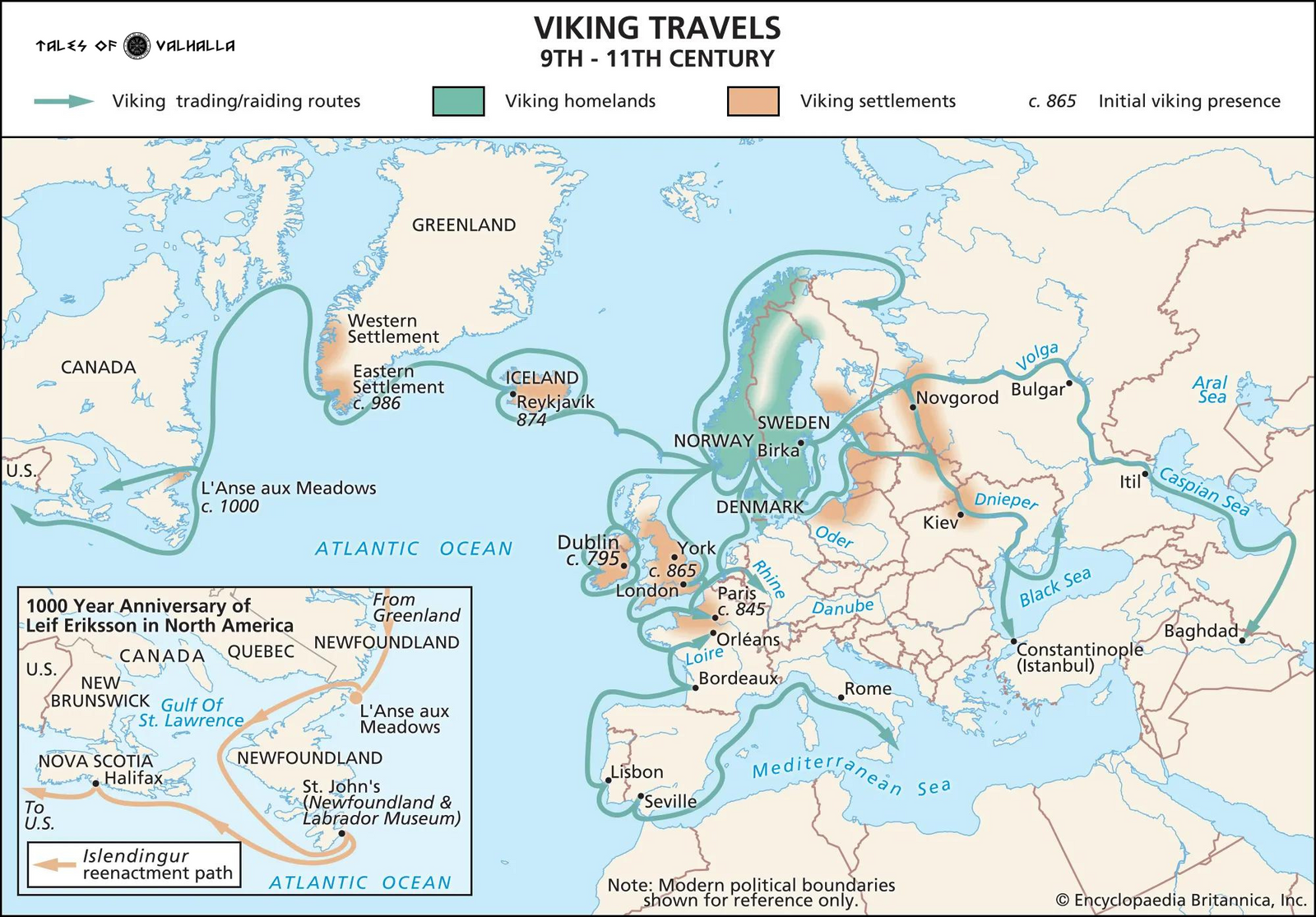
Map of Viking expansion between the 8th and 11th century
Who Were the Vikings?
The Vikings were a seafaring people from the Scandinavian region, known for their explorations, trading routes, and raids across Europe between the 8th and 11th centuries. They were not just pirates and warriors but also skilled traders, explorers, and settlers. The term "Viking" actually refers to the activity of raiding or piracy, rather than a specific ethnic group or nationality. This activity was predominantly carried out by Norsemen, the ancestors of modern Scandinavians.
Where Did the Vikings Come From?
The Vikings originated from Scandinavia, a region that includes present-day Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. These lands, with their rugged coastlines and fjords, provided the perfect backdrop for a people who were destined to become some of history's greatest sailors and explorers.
Norway, Sweden, and Denmark: The Heart of Viking Lands
- Norway: Known for its dramatic fjords and harsh winters, Norway was home to many of the most famous Viking explorers, including Leif Erikson, who is credited with discovering North America long before Columbus.
- Sweden: The Vikings from Sweden were primarily traders and explorers, traveling eastward into what is now Russia and even reaching the Byzantine Empire.
- Denmark: Danish Vikings were notorious for their raids on England and their eventual settlement in parts of the British Isles.
When Did the Viking Age Begin?
The Viking Age is generally considered to have begun in 793 AD, with the infamous raid on the Lindisfarne monastery in England. This event marked the start of a period of nearly 300 years during which Viking warriors, traders, and explorers left an indelible mark on Europe. The age came to an end around 1066 AD, with the Norman Conquest of England, which was led by William the Conqueror, himself a descendant of Viking settlers.
Viking Culture and Society
 Viking Culture and Society
Viking Culture and Society
Norse Mythology and Beliefs
Norse mythology played a central role in Viking culture. The Norse gods, such as Odin, Thor, and Freyja, were revered and their stories passed down through generations. These myths not only provided explanations for natural phenomena but also guided the Vikings' understanding of honor, bravery, and fate. Rituals, sacrifices, and festivals were all part of their religious practice, closely tied to the land and sea that dominated their lives.
Viking Society: Warriors, Farmers, and Explorers
Viking society was multifaceted, with people taking on various roles depending on the season and circumstances. While many are famous for their roles as warriors, the majority of Vikings were farmers and fishermen, who relied on the land and sea for sustenance.
The Role of Women in Viking Society
Viking women held a relatively high status compared to their counterparts in other contemporary societies. They could own land, initiate divorce, and were often responsible for managing the household in the absence of men. Some women, known as shieldmaidens, even took up arms and fought alongside men in battle, although their exact role in warfare is still debated among historians.
Is Viking Not Norse? Understanding the Terminology
 Is Viking Not Norse? Understanding the Terminology
Is Viking Not Norse? Understanding the Terminology
The Term ‘Viking’ Explained
The word "Viking" comes from the Old Norse word "vikingr," meaning a pirate or raider. It refers to the activities these Norsemen engaged in rather than a distinct group of people. Therefore, not all Norsemen were Vikings, but those who went "a-viking" were typically involved in seafaring raids, trading, or exploration.
Norse: The Cultural Identity
"Norse" refers to the people and culture of Scandinavia during the Viking Age. The Norse were the ancestors of modern-day Scandinavians and were known for their distinct language, Old Norse, and their rich mythology. The Norse identity encompasses more than just the activities of the Vikings; it includes the entire cultural and social fabric of the Scandinavian people during this period.
Nordic vs Scandinavian: What’s the Difference?
The terms "Nordic" and "Scandinavian" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. "Scandinavian" refers specifically to the countries of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. In contrast, "Nordic" is a broader term that includes not only these three countries but also Iceland and Finland.
Modern-Day Nordic Countries
Today, the Nordic countries are known for their high standard of living, social welfare systems, and strong cultural identities. The Viking legacy is still evident in many aspects of Nordic culture, from place names to modern interpretations of Norse mythology.
Viking Legacy: From Raids to Settlements
 Viking Legacy: From Raids to Settlements
Viking Legacy: From Raids to Settlements
Viking Expansion Across Europe
The Vikings were not content to stay within the confines of Scandinavia. Their longships, capable of navigating both open seas and shallow rivers, allowed them to travel far and wide. They established trade routes that extended from the British Isles to the Byzantine Empire and even reached the shores of North America.
Viking Influence on Modern Culture
The influence of the Vikings extends far beyond their time. They left a lasting impact on the regions they settled, including parts of England, Scotland, Ireland, and France. Their legacy can be seen in the languages, place names, and even genetic makeup of these areas.
Viking Remnants in Place Names
Many place names in the British Isles, particularly in England and Scotland, have Viking origins. For example, names ending in "-by" (such as Derby and Whitby) are derived from the Old Norse word for "village" or "settlement." This is a testament to the lasting impact of Viking settlements in these regions.
Conclusion
The Vikings were a product of their environment—rugged, resourceful, and ready to explore the world beyond their Scandinavian homeland. Their legacy, from the sagas of Norse mythology to the enduring influence on place names and cultures, continues to captivate our imagination. By understanding where the Vikings came from and the cultural forces that shaped them, we gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable chapter in history.