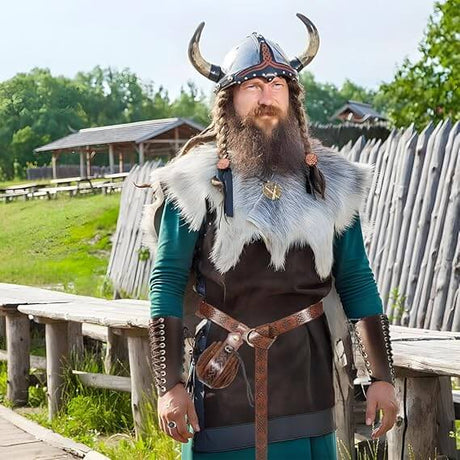
Close your eyes and picture a Viking. What do you see? For most of us in the United States, a powerful and specific image comes to mind, sculpted by decades of movies, television, and popular art: a towering giant of a man, at least six and a half feet tall, with a cascade of wild, blonde hair, piercing blue eyes, and a ruggedly handsome (or fearsomely brutish) face. He’s clad in rough furs and leather, and, of course, crowned with a horned helmet. It’s a compelling and iconic image. But what did the Vikings look like in reality?
The truth, unearthed from thousand-year-old gravesites and pieced together through cutting-edge science, is far more complex, diverse, and fascinating than any simple stereotype. To truly answer the question, "What did the Vikings look like?", we must embark on a journey of historical and archaeological discovery. We will strip away the layers of myth and misconception to reconstruct the faces, figures, and fashions of the people of the Viking Age.
Deconstructing the Myth: The Viking of Popular Culture
The modern image of the Viking is a powerful cultural shorthand, but it's a composite, blending historical fragments with romantic fantasy. This larger-than-life figure is often defined by:
- Gigantic Stature: They are almost always portrayed as towering over their enemies.
- Uniform Appearance: Typically shown as exclusively blonde and blue-eyed.
- Rugged (and Dirty) Demeanor: Often depicted as unkempt, with wild hair and beards, clad in rough, practical furs.
- The Horned Helmet: The quintessential, yet completely inaccurate, piece of Viking headwear.
While this makes for great entertainment, it obscures the more nuanced and interesting reality. So, let’s tackle each of these elements and find out what did the Vikings look like according to the evidence.

Deconstructing the Myth: The Viking of Popular Culture
The Foundation: How Tall Were the Vikings?
One of the most persistent questions is about their height. Were they the giants of the medieval world? The answer lies in their bones.
The Science of Skeletons: Measuring the Past
Archaeologists and physical anthropologists determine the stature of ancient peoples through osteology, the study of bones.
- Long Bone Measurement: The length of the major long bones—specifically the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (shin bone)—has a strong and predictable correlation with a person's living height.
- Scientific Formulae: By applying established regression formulae to these measurements, scientists can calculate a remarkably accurate estimate of an individual's height. This scientific approach gives us the most reliable data we have to answer "What did the Vikings look like?" in terms of stature.
The Verdict: Taller Than Their Times, But Not Giants
Based on numerous studies of skeletons from Viking Age graves across Scandinavia, the average heights were:
- Viking Men: Approximately 170 to 176 centimeters (cm), which translates to roughly 5 feet 7 inches to 5 feet 9 inches.
- Viking Women: Approximately 158 to 165 centimeters (cm), which translates to roughly 5 feet 2 inches to 5 feet 5 inches.
While these numbers might seem average by modern American standards, the crucial context is how they compared to other medieval Europeans. In an era when poor nutrition was rampant in many parts of Europe, the Vikings were often a head taller than the people they encountered in England, France, and Germany. This height advantage, combined with their robust build, would have made them appear physically imposing and undoubtedly contributed to their fearsome reputation. So, while not mythical giants, they were often the taller people in the room (or on the battlefield).
A Palette of the North: Hair and Eye Color
The "blonde bombshell" stereotype is perhaps the most enduring visual myth about the Vikings. The reality, as revealed by modern genetics, was far more colorful. The question "What did the Vikings look like?" has a much more diverse answer when it comes to hair color.
Busting the Blonde Myth
While blonde hair was certainly present and likely prized in Norse culture (as suggested by some saga descriptions of heroes), it was by no means universal.
The Genetic Evidence: A Landmark Study
A groundbreaking 2020 study published in the journal Nature analyzed the DNA from over 400 Viking Age skeletons. The results completely overturned the blonde stereotype:
- Brown Hair was Most Common: The genetic analysis revealed that brown hair was the most common hair color among the Viking Age population.
- A Spectrum of Colors: The study also found genes for blonde, red, and black hair, confirming a diverse palette of hair colors.
- Regional Variations: There were also regional differences. For example, Vikings from the Swedish regions showed a higher prevalence of blonde hair, while Norwegian and Danish Vikings had a higher frequency of red and brown hair.
- A Mixed Gene Pool: The study also proved that the Vikings were not a single, isolated genetic group. There was significant gene flow from Southern Europe and even Asia into Scandinavia, and from Scandinavia into the rest of Europe. This mixing further contributed to their diverse appearance.
The Role of Hair Bleaching
Intriguingly, there is also evidence that some Vikings, particularly men, artificially lightened their hair.
- Lye Soap: Historical accounts and archaeological chemistry suggest they used a strong soap with a high lye content. This potent substance would strip pigment from the hair, bleaching it to a lighter blonde or, depending on the original hair color, a reddish shade.
- Why Bleach? The motivations were likely twofold. Firstly, it could have been a beauty standard, a way to achieve the culturally prized blonde look. Secondly, and perhaps more practically, the harsh lye soap was an effective way to kill and prevent head lice. This detail adds a fascinating layer to the question of "What did the Vikings look like?"
The Face of the Viking: Features and Complexion
What about their facial features? Thanks to archaeological finds and modern reconstruction techniques, we can get a surprisingly clear idea.

The Face of the Viking: Features and Complexion
Reconstructing Faces from Skulls
Using forensic techniques, scientists can take a well-preserved Viking Age skull and reconstruct the facial features. These reconstructions often reveal faces that are both familiar and strikingly different from modern stereotypes.
- Common Features: These reconstructions, combined with skeletal analysis, often show strong facial structures: well-defined jawlines, prominent brow ridges (especially in males), and high cheekbones. However, there was a wide range of facial types, just as there is in modern Scandinavia.
- Skin Tone: Based on genetic evidence and contemporary accounts like that of Ibn Fadlan (who described the Rus' as "fair and reddish"), the Vikings likely had fair skin that was prone to ruddiness from exposure to the sun and wind.
More Than a Messy Mane: Grooming, Hygiene, and Adornment
This is where we confront the "dirty barbarian" myth head-on. The idea that Vikings were unkempt and filthy is demonstrably false. The archaeological record tells a story of a people who cared deeply about their appearance and personal hygiene.
The Archaeological Proof of Grooming
- Combs, Combs, and More Combs: Combs are one of the most common artifacts found in Viking Age graves, for both men and women. These weren't crude tools; many were beautifully crafted from antler, bone, or wood, and kept in protective cases. This indicates that daily hair and beard combing was a standard practice.
- Grooming Kits: It was common for Vikings to be buried with personal "grooming kits," which could include tweezers, razors, and small, delicate "ear spoons" used for cleaning earwax.
Viking Hairstyles and Beards
The evidence suggests that Viking hairstyles were intentional and well-maintained.
- Men's Styles: Men often wore their hair long, a sign of freedom and status. A specific style mentioned in historical sources and seen in carvings is a sort of "reverse mullet" – long in the back and on top, but with the front and sides of the head shaved. Beards were a mark of manhood and were combed, styled (sometimes braided or forked), and likely oiled.
- Women's Styles: Women also prized long hair, which they often wore in intricate braids or tied up in knots at the back of the head, a practical style for a life of work. They sometimes wove colored ribbons into their hair. Married women typically wore a head covering, such as a scarf or cap.
Tattoos and Kohl? A Surprising Twist
The quest to answer "What did the Vikings look like?" also involves looking at their skin and eyes.
- Tattoos: As mentioned, the account of Ibn Fadlan strongly suggests that at least some Vikings (the Rus') practiced extensive tattooing.
- Kohl Eyeliner: In the same account, Ibn Fadlan noted that both men and women wore kohl, a dark cosmetic, around their eyes to enhance their beauty and make their gaze more intense. This practice, likely adopted from contact with Middle Eastern cultures, shatters the image of a purely rustic people.
Story Vignette: A Warrior's Morning Bjorn the warrior awoke with the first light filtering through the smoke hole of the longhouse. His morning ritual was as ingrained as his battle training. He splashed his face with cold water from a wooden basin. Taking a fine comb carved from elk antler, he meticulously worked through his long, brown beard, untangling the knots from sleep. He then combed his hair, which was shaved at the sides but long on top, tying the top section back with a simple leather thong. Finally, he took a small pot of kohl and a stick, carefully applying a dark line around his eyes. It was a look of controlled fierceness. His appearance was a part of his identity, a declaration of his status as a warrior who was well-groomed and ready for whatever the day might bring. This daily routine was as much a part of what the Vikings look like as their armor or weapons.
Dressed for Success (and Survival): What Did Vikings Wear?
The clothing of the Vikings was far from the drab, furry loincloths of fantasy. It was practical, layered, and often surprisingly colorful.
- Practical and Colorful Fabrics: The primary materials were wool and linen. Wool provided essential warmth and was naturally water-resistant, while linen was used for undergarments. Using a variety of natural dyes from plants like woad (blue), madder (red), and weld (yellow), they created clothing in a range of vibrant colors.
- Typical Garments: Men typically wore a tunic and trousers. Women wore a long underdress (usually linen) with a distinctive overdress (a wool "apron dress" or hangerok) held up by straps and fastened at the shoulders with large, ornate brooches. Both sexes wore cloaks for warmth, fastened with a pin or brooch.
- Jewelry as Status: Jewelry was a key part of their appearance and a primary way to display wealth. Both men and women wore brooches, rings, necklaces, and arm-rings, often made of silver or, for the very elite, gold.
A Comparative Summary: The Hollywood Viking vs. The Historical Viking
To make the answer to "What did the Vikings look like?" as clear as possible, let's compare the myth to the reality.
Why Does It Matter What the Vikings Look Like?
Moving beyond the stereotypes to find a more accurate answer to "What did the Vikings look like?" is important for several reasons.
Humanizing the Past
When we strip away the one-dimensional caricature of the "brutal barbarian," we begin to see the Vikings as they were: real, complex human beings. They were parents, farmers, craftsmen, poets, and traders who cared about their families, their homes, and their appearance. This makes their history far more relatable and interesting.
Understanding Diversity
Recognizing their physical and cultural diversity is crucial. The Viking world was not a monolith. It was a dynamic and interconnected network of communities with a mixed gene pool and varied customs. Acknowledging this diversity gives us a much richer and more accurate picture of the Viking Age.
Conclusion
So, what did Vikings look like? Not dirty savages, but tall, robust people who valued grooming, wore colorful clothes, and adorned themselves with jewelry. They were diverse—brown hair most common—and their appearance reflected a hardy lifestyle and rich heritage.
The stereotype is simple, but the truth is richer. At Tales of Valhalla, we celebrate the real Vikings—human, complex, and far more fascinating than myth.