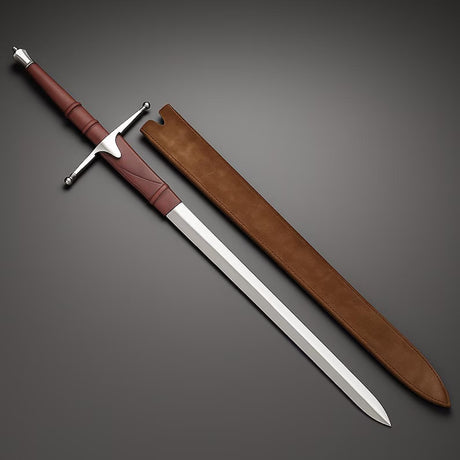
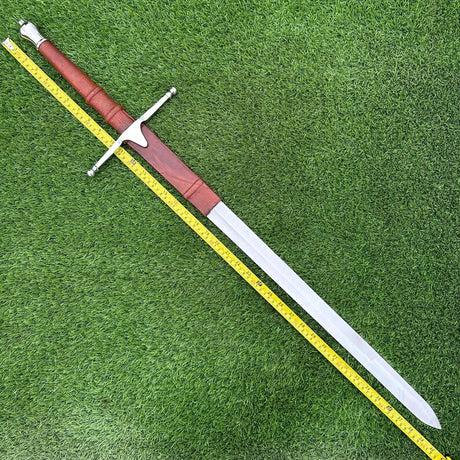
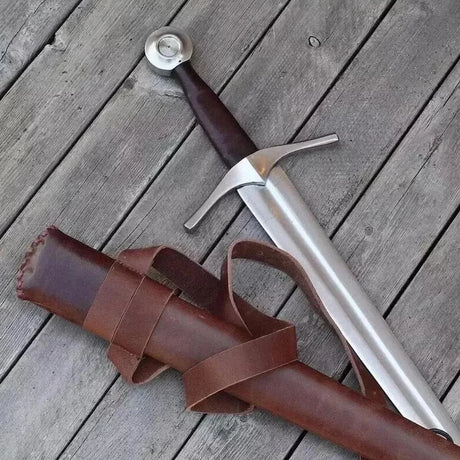
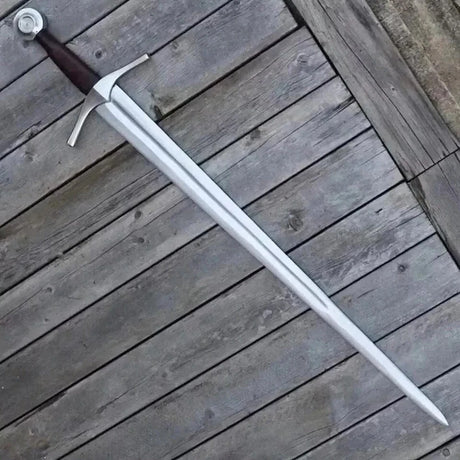
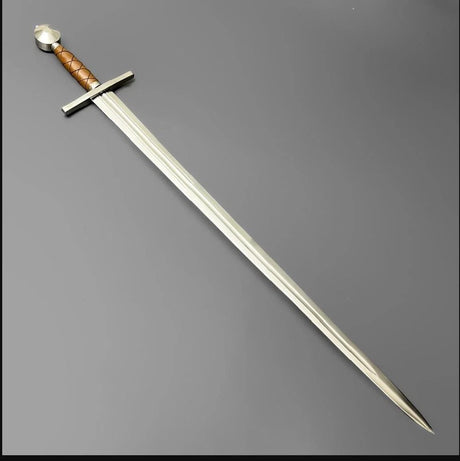
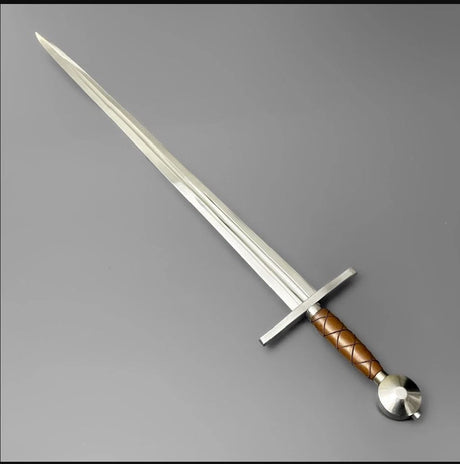
The Viking sword is a symbol of power, honor, and craftsmanship in Norse history. More than just a weapon, it evolved through centuries of innovation, reflecting the cultural and technological advancements of the Viking Age. This blog will explore the rich history and evolution of the Viking sword, discussing its origins, development, and lasting legacy.
The Early Origins of the Viking Sword
From Roman Influence to Norse Design
The history of the Viking sword traces back to earlier weapon designs influenced by the Roman Empire. The early Norse swords, often referred to as spatha, were long, straight, double-edged blades primarily designed for slashing. These swords were modeled after Roman and Germanic designs, but the Vikings soon began to adapt the swords to suit their needs, giving rise to the classic Norse sword that became emblematic of Viking warfare.
These early Viking swords were simple, functional weapons made primarily from iron. They were built to endure the harsh conditions of battle, able to cut through shields and armor, and were perfect for close-quarters combat. The lack of elaborate designs at this stage reflects their primary role as essential tools of war.
However, as Viking culture developed, so did their swords. The swordsmiths of the Viking Age were artisans, continually improving both the functionality and the aesthetics of their weapons. This combination of practicality and artistry began to define the evolution of the Viking sword, marking the transition from a basic tool to a symbol of power and prestige.
- See more: Viking Swords Collection
The Importance of Swords in Viking Society
Unlike more common weapons like spears or axes, Viking swords were rare and expensive. The creation of a sword required both high-quality materials and expert craftsmanship, making them luxury items reserved for the wealthy elite. As a result, swords were status symbols in Viking society, representing power, wealth, and honor.
For Viking warriors, owning a sword was a mark of distinction. Many of these swords were personalized with names and adorned with symbols that reflected their owner’s status and achievements. Swords were often passed down from generation to generation, becoming family heirlooms imbued with history and legend.
Swords also played a ceremonial role in Viking society. They were used in religious rites and as offerings to the gods, symbolizing the spiritual connection between warriors and their weapons. The Viking sword, therefore, represented more than just a tool for battle—it embodied the very essence of the Viking warrior's identity.
The Evolution of Viking Sword Craftsmanship
The Technique of Pattern Welding
One of the key innovations in Viking sword-making was the technique of pattern welding. This process involved twisting and folding strips of iron and steel together, creating a blade that was both strong and flexible. The resulting swords featured distinctive wave-like patterns along the blade, which were not only aesthetically pleasing but also indicative of high-quality craftsmanship.
Pattern-welded Viking swords were prized for their durability and beauty. The intricate patterns were a testament to the skill of the swordsmith, who had to carefully balance the strength of the blade with its flexibility. A well-made sword needed to be tough enough to withstand the impact of battle but also flexible enough to avoid shattering under stress.
The Viking smiths who mastered the art of pattern welding were highly respected in their communities. Their swords were often commissioned by kings, chieftains, and other elite warriors who sought weapons that reflected their status and power. This craftsmanship became a hallmark of Viking culture and contributed to the sword’s iconic status in Viking history.
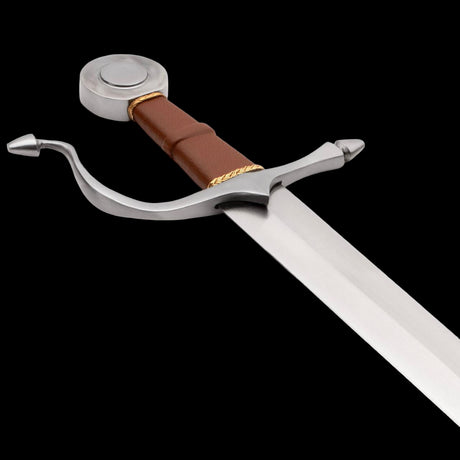
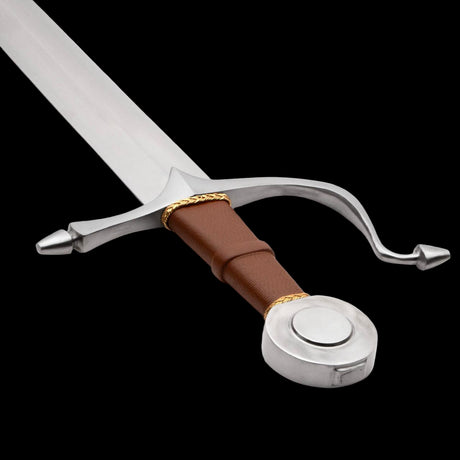
The Hilt and Pommel: Form and Function
The hilt and pommel of the Viking sword were as important as the blade itself. Early Viking swords had relatively simple hilts, often made from wood or bone, designed for practical use in battle. However, as the Viking Age progressed, hilts became more elaborate, adorned with precious metals, carvings, and runes.
The pommel—the knob at the end of the hilt—served both a practical and decorative purpose. It acted as a counterweight to the blade, helping to balance the sword and making it easier to wield. At the same time, the pommel was often engraved or decorated with intricate designs, reflecting the sword’s status as a work of art.
In many cases, the hilt and pommel were personalized to reflect the identity of the sword’s owner. Runes and symbols were inscribed into the hilt, invoking the protection of the gods or commemorating great deeds performed with the sword. This personalization made each Viking sword unique, transforming it into a cherished possession that was both functional and symbolic.
The Transition from Iron to Steel
The Rise of Steel Swords
As the Viking Age progressed, the development of steel technology transformed sword-making. Early Viking swords were made from iron, which, while strong, was prone to rust and wear. Steel, on the other hand, offered superior strength, durability, and the ability to hold a sharper edge for longer periods. The evolution of the Viking sword took a significant leap forward with the advent of steel swords.
The process of creating steel swords was more complex than that of iron swords, requiring precise control over heat and materials. Viking swordsmiths learned to mix iron with carbon to create steel, which allowed for the creation of harder and more resilient blades. These steel swords became prized possessions, offering a significant advantage in battle.
One of the most notable advancements in this period was the development of crucible steel, a high-quality steel used to make the legendary Ulfberht swords. These swords were much stronger and more flexible than their iron counterparts, making them some of the most coveted weapons of the Viking Age.
Ulfberht: The Pinnacle of Viking Sword Craftsmanship
The Ulfberht sword is one of the most famous examples of Viking sword technology. Made from high-quality crucible steel, these swords were far ahead of their time. The unique steel composition made them incredibly strong and flexible, allowing them to cut through armor and shields with ease.
What makes the Ulfberht swords even more remarkable is the mystery surrounding their origins. The name “Ulfberht” was inscribed on the blades, leading scholars to believe that these swords were made by a specific master swordsmith or a group of smiths. Over 170 Ulfberht swords have been discovered, but the technology used to create them was not available in Europe until centuries later, suggesting that the Vikings may have acquired this technology through trade or raids in the Middle East.
Ulfberht swords were rare and highly prized, often owned by kings and elite warriors. The discovery of these swords in Viking graves and battlefields underscores their importance in Viking society and their enduring legacy as symbols of Viking prowess.
The Evolution of Viking Sword Design
From Wide Blades to Tapered Edges
The early Viking sword featured a broad, straight blade, designed primarily for slashing in battle. These blades were effective in close-quarters combat, where powerful blows could cut through armor and shields. However, as warfare evolved, so did the shape of Viking swords.
By the later Viking Age, swords began to feature more tapered, pointed blades. This design allowed for greater versatility in battle, enabling both slashing and thrusting attacks. The development of pointed blades was a response to changing combat tactics, as Viking warriors began to face enemies who used more advanced armor and defensive strategies.
This evolution in blade design reflects the adaptability of Viking warfare. As the Vikings encountered new challenges on the battlefield, they responded by improving their weapons, ensuring that their swords remained effective in both offensive and defensive combat.
The Fuller: Reducing Weight Without Sacrificing Strength
Another key development in Viking sword design was the introduction of the fuller—a groove that runs down the center of the blade. The fuller, sometimes referred to as a “blood groove,” was designed to make the sword lighter without sacrificing its strength. By removing some of the metal from the center of the blade, swordsmiths were able to create a more agile weapon that was easier to wield in battle.
The fuller also helped to balance the sword, making it more maneuverable in the hands of the warrior. This design feature became a hallmark of Viking swords and contributed to their effectiveness in battle. The ability to reduce weight while maintaining strength made Viking swords some of the most versatile weapons of their time.
The Viking Sword in Battle
Sword Combat and the Shield Wall
The Viking sword played a crucial role in the shield wall, a defensive formation used by Viking warriors. In this tactic, warriors would lock their shields together, creating an impenetrable barrier against enemy attacks. The warriors behind the shields would use their swords to strike over or around the shields, targeting the enemy’s vulnerable areas.
The relatively short length of the Viking sword made it ideal for this type of combat. Warriors could deliver quick, powerful strikes in the close confines of the shield wall, using their swords to cut through armor and flesh. The sharp, double-edged blade of the Viking sword was well-suited for both slashing and thrusting, making it a versatile weapon in battle.
Famous Viking Battles Featuring Swords
Throughout Viking history, swords were at the forefront of many famous battles. From the raids on England and France to the battles for control of the North Sea, Viking swords played a critical role in shaping the outcomes of these conflicts. One of the most famous battles in Viking history is the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, where Viking warriors, armed with their swords, fought against the English army. Although the Vikings ultimately lost, the battle demonstrated the skill and ferocity of Viking swordsmanship.
The Legacy of the Viking Sword
Viking Swords as Cultural Artifacts
Today, Viking swords are among the most valuable and sought-after artifacts from the Viking Age. These swords, many of which have been discovered in burial sites, offer insight into the lives of Viking warriors and the societies they lived in. The craftsmanship and artistry of these swords, combined with their historical significance, make them some of the most iconic weapons in history.
Many Viking swords have been preserved in museums around the world, where they are studied and admired by historians and enthusiasts alike. The discovery of these swords in Viking graves and battlefields has helped archaeologists piece together the history of Viking warfare and culture.
Modern Replicas and Viking Sword Collecting
For those fascinated by Viking history, owning a Viking sword replica is a way to connect with the past. Modern craftsmen create authentic Viking sword replicas using traditional techniques, offering collectors and enthusiasts the opportunity to own a piece of Viking history.
These replicas are made from high-quality materials and feature the same designs that Viking warriors would have used in battle. Whether for display, reenactment, or historical study, Viking sword replicas continue to captivate the imagination of people around the world.
Conclusion
The Viking sword is more than just a weapon—it is a symbol of the Viking spirit, proudly celebrated by Tales of Valhalla. These swords evolved over centuries, adapting to the changing needs of Viking warriors while maintaining their status as icons of power, honor, and craftsmanship. From early iron blades to the advanced technology of Ulfberht swords, Viking swords embody the ingenuity and warrior culture of the Viking Age.
Today, Viking swords continue to inspire awe and admiration. Whether displayed in a museum or wielded in historical reenactments, these swords remain an enduring symbol of a time when warriors ruled the seas, reflecting their strength and courage.
FAQs
1. What were the earliest Viking swords like?
Early Viking swords (around 8th-9th centuries) were often simpler in design, with a straight, double-edged blade and a relatively short grip. They were primarily slashing weapons, reflecting the influence of earlier Germanic swords. These swords often had pattern-welded blades, a technique involving twisting and forging different iron types together for strength and visual appeal.
2. How did Viking swords change over time?
Viking swords evolved throughout the Viking Age (roughly 8th-11th centuries). Blades became longer, slimmer, and more tapered, with a pronounced fuller (a groove running down the length of the blade) to reduce weight and increase flexibility. The hilts also became more elaborate, with intricately decorated pommels and guards.
3. What were the most famous types of Viking swords?
Some of the most renowned Viking swords include the Ulfberht swords, known for their superior quality and craftsmanship, and the Oakeshott Type X swords, characterized by their longer, more tapered blades and cruciform hilts.
4. What influenced the development of Viking swords?
The evolution of Viking swords was influenced by various factors, including contact with other cultures through trade and raiding. They incorporated elements from Frankish and Carolingian swords, leading to more complex hilt designs and improved blade construction.
5. What were Viking swords used for?
Viking swords were primarily weapons of war, used in battles and raids. However, they were also symbols of status and wealth. A high-quality sword was a prized possession, often passed down through generations or given as a prestigious gift.
6. Where can I see examples of Viking swords today?
Many museums around the world house impressive collections of Viking swords. Some notable institutions include the National Museum of Denmark in Copenhagen, the Viking Ship Museum in Oslo, and the British Museum in London.